
Internet privacy is paramount these days and internet cookies always seem to be in the news. I wanted to find out about using a VPN to protect against cookies was a good idea or not, as I wanted to make sure my privacy was protected.
Does a VPN protect you from cookies? A VPN does not protect you from cookies being placed on your device, a VPN cannot remove existing cookies either. The VPN provides a secure connection to protect privacy across the internet by using encryption and assigning a fake IP address, so the real IP address won’t be visible to the websites being visited.
Cookies won’t be stopped in their tracks when using a VPN as these will still be allowed to be stored by the devices web browser. A lot of the functionality required for websites needs cookies, to remember what was done the last time the website being visited to personalisations made.
That being said, some websites will still use cookies in a way that can affect your privacy, by using them to track web browsing habits, with some third-party cookies being reknowned for this type of behaviour.
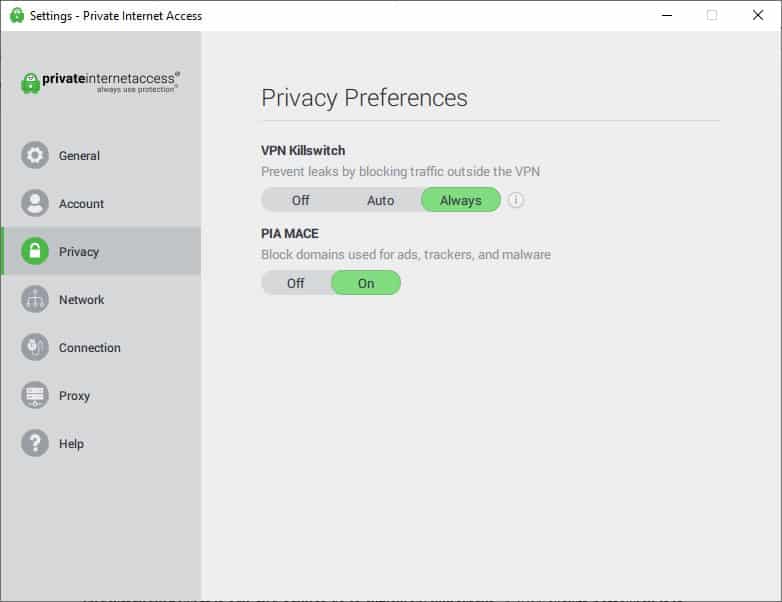
Some VPNs can block access to domains used for adverts, tracking cookies and malware like Private Internet Access (PIA). PIA’s MACE technology uses threat intelligence about domains, that’s just a list of known suspect domains, so if the domain verydangerouswebsite.rus has tracking cookies used as spyware then any attempt made to connect to this domain will be blocked by PIA.
Even if the domain is being accessed from another domain, such as an advert link from a webpage on a safe website (adverts on websites are sometimes bought by criminals to entice people to their dodgy websites).
Do cookies work with VPN? Cookies will still work with a VPN as the web browser will carry on being able to receive cookies from the websites being visited. The VPN is not altering any of the web traffic being sent from your web browser to the internet, it is just providing encrypted communication channel to the VPN server.
Cookies are essential with many websites in remembering previous visits and no VPN will ever try to stop cookies from being set, as the web browsing experience will be severely hampered.
What are cookies?
It’s important to understand what cookies are and the purpose they serve. Cookies are small text files that provide a way for websites to store information on the users web browser. When a user revisits the website, the website can use the cookies to find out if the user has visited the website before and set any preferences made previously.
The website can also use the cookie to tailor the website for the user, as the user may have made some personalization changes. I use a popular tech news website and by default this website has a dark background with light text. I’m not a big fan of dark backgrounds and find it difficult on the eye to read the content. Fortunately, there is an option to change this and I have clicked on the option at the bottom of the website to change it to a light background and dark text.
Eveytime I revisit the website, I am greeted by a light background and dark text but if I delete my cookies, my next visit defaults to the dark background with light text. The cookie set by the website in my web browser contains my preferences and eveytime I visit the website, the cookie is checked and the preferences automatically set.
Everytime I revisit a website where I haven’t quite finished shopping, the shopping cart contains the items I’ve chosen but not yet paid for. The shopping cart isn’t really remembering what I selected, it’s using cookies stored on my web browser and reading the associated text file to see which items I added to the shopping cart.
Some website can use cookies to record the time you spent on their website, so everytime you revisit they know how long you spent last time and can tailor special offers for example, to be more appealing. Or maybe, they realize you are a regular user so they don’t give you any of the introductory first time visitor offers.
With websites whrre a login is required, having to remember your username and password each time can be a pain, but if the remember me button is selected, the username and password are saved into a cookie file on the web browser.
Hopefully the website has used some form of encryption to save this information in the cookie, so prying eyes can prise this information out. Now, everytime the website is revisted, an automatic login occurs using the userbame and password information in the cookie.
Are cookies dangerous?
Cookies can be dangerous if they are used for tracking purposes as they are able to identify users browsing habits, that can then be used for targeted advertising. Cookies can also be used to store information about the users device, web browser, location to build up a digital fingerprint. This digital fingerprint will provide a unique identity that can be tracked and used to determine browsing habits.
Incorrectly set cookies can reveal sensitive information, like for example leaving username and password details in a cookie instead of a session token. This could allow third-party cookies to read cookies across websites and see the cookie contents and try to use these maliciously if they wanted to.
Why cookies are needed?
Cookies are needed to keep track on user preferences, allow automatic logon to websites when the ‘remember me’ tick box has been previously checked to remembering shopping cart items and previous orders for the next time you visit the website.
The Internet is stateless in that websites don’t remember the previous state, that is they don’t remember what you did on your last visit. Cookies provide a mechanism of remembering the previous state of things, allowing websites to ‘remember’, actions and transactions from before.
This is particularly important with websites where you haven’t logged into before, as having an account with the website is one way of keeping tabs on your history with the website. If you’ve used guest access to buy something for example, the next time you visit the website, because you don’t log into the website, it has no idea who you are. However, if the website has left a cookie identifying you as someone with a previous guest account transaction, the website knows who you are.
Without cookies, everytime you visit a website any previous history will be unknown so any incomplete transactions for example, like a shopping cart that hasn’t been checked out will not be known.
Are tracking cookies dangerous?
Tracking cookies can be dangerous as they keep a record of identifying features such as the web browser being used, the location, real IP address, the browsing activity to a whole host of other data used to fingerprint the user. This data can reveal a lot about a person and can be used in targetted advertising, allowing advertisers to pay for advertising only for people who meet their specific criteria, leading to better returns on their advertising investments.
A famous politician found out the hard way about tracking cookies when he went on to a fellow politicians website and noticed adverts for Thai brides on every page he visited. He then used his Twitter account to tell his followers (and the world) that the fellow politician had Thai bride adverts on his website.
It was when he was ridiculed on twitter and in the national press, and told that advertising tracking cookies had recorded his web browsing activities and any website he visited where there were adverts with the same advertiser as the tracking cookies, they would show adverts relevant to his searches.
How do I block all cookies?
There are number of ways to block all cookies and these include not always logging into websites like Google and Facebook, using Private Browsing features provided by popular web browsers, using enhanced tracking cookie protection to using different devices for different types of web browsing.
Don’t log into websites
By logging into websites like Google and Facebook, allows these websites to track your browsing habits to some extent. Facebook particularly uses tracking cookies to be able to tailor the advertising appearing on the websites and Google too uses powerful analytical cookies to obtain data.
Use private browsing
Private Browsing in Mozilla Firefox and Incognito Mode in Google’s Chrome browser allow cookies to be stored only for the duration of the browsing session and upon exit the cookies, browsing history and any search history are deleted.

Many people do make the mistake of thinking private browsing keeps them anonymous but it doesn’t as their real IP address is used when connections to websites are made, so their Internet Service Provider (ISP) can see their browsing habits.
Enhanced tracking cookie protection
Some web browsers can provide additional tracking cookie protections where tracking cookies are actibely blocked depending on the privacy settings chosen (as shown in screenshot below).
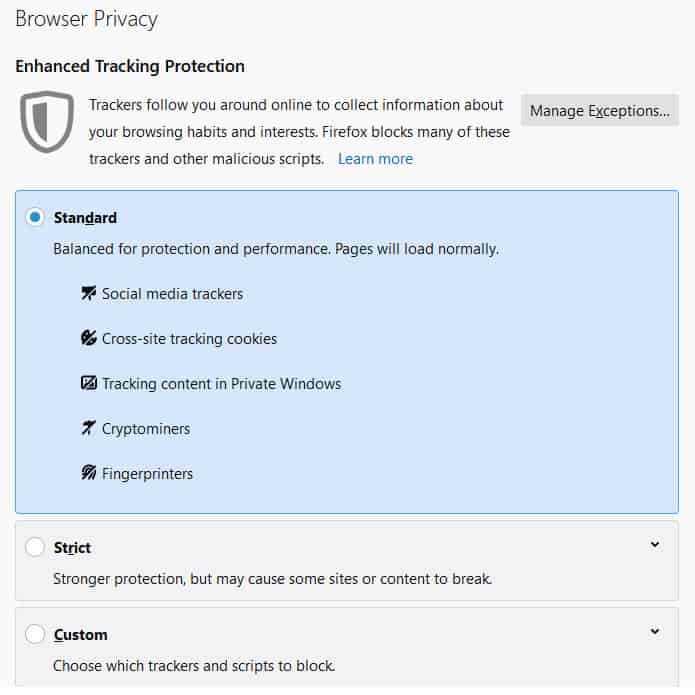
With customisable settings for websites known for agressively using tracking cookies to track bisitors available, the scope for protection against tracking cookies is increased.
Use different devices
Sometimes it may be prevalent to use different devices for different internet activities, I tend to use a different laptop for any personal activities like banking, bill payments and so on. With another laptop or my smartphone for normal browsing activities. This makes it difficult for any cookies to build up a complete profile of my advertising habits.
How does a VPN affect cookies?
In conclusion a VPN generally does not affect cookies and allows cookies to be used for storing information that is useful for the next visit. Information like previous orders, shopping carts that haven’t been checked out to color changes and preferences of the website itself.
Some VPNs like Private Internet Access have functionality to block malicious cookies from suspect domains using threat intelligence (an up to date list of bad domains). This can help in protecting against tracking cookies and malware.

